Dwarf planets are a category of celestial objects that are similar to planets, but are smaller in size and lack certain characteristics that define a planet. The classification of a celestial object as a dwarf planet was introduced by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2006.
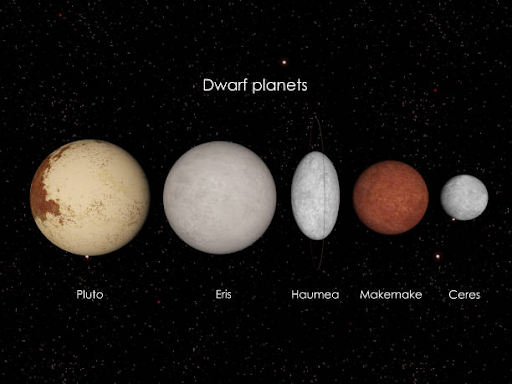
The IAU defines a dwarf planet as a celestial body that orbits the Sun, is spherical in shape, and has not cleared its orbit of other debris. This means that while a dwarf planet is similar to a planet in terms of its shape and orbit, it has not become dominant in its orbit and there are other objects in its vicinity. Currently, there are five officially recognized dwarf planets in our Solar System: Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, and Ceres.
Source - Shutterstock Images
Pluto is the most well-known dwarf planet and was formerly considered the ninth planet in our Solar System. It was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006 due to its size and orbit. Pluto is located in the Kuiper Belt, a region beyond Neptune that contains many icy objects. It has five known moons and a highly eccentric orbit that brings it closer to the Sun than Neptune for part of its orbit.
Eris is the largest known dwarf planet and is located in the scattered disc, a region beyond Neptune that contains many objects with highly elliptical orbits. It was discovered in 2005 and is named after the Greek goddess of discord. Eris has one known moon and a highly elliptical orbit that takes it far beyond Pluto.
Haumea is a dwarf planet located in the Kuiper Belt. It is named after the Hawaiian goddess of childbirth and fertility. Haumea has an elongated shape and rotates rapidly, completing a full rotation in just four hours. It has two known moons and a highly elliptical orbit.
Makemake is another dwarf planet located in the Kuiper Belt. It was discovered in 2005 and is named after the creation deity of the Rapa Nui people of Easter Island. Makemake is one of the largest known objects in the Kuiper Belt and has a highly reflective surface.
Ceres is the only dwarf planet located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. It was the first object to be discovered in the asteroid belt and was considered a planet for a brief period in the 19th century before its size was determined. Ceres is the largest object in the asteroid belt and has a rocky surface.
In addition to these five recognized dwarf planets, there are many other objects in our Solar System that could potentially be classified as dwarf planets. These include objects in the Kuiper Belt, the scattered disc, and even some of the larger asteroids in the asteroid belt.
The study of dwarf planets is important because they provide valuable information about the formation and evolution of our Solar System. Many dwarf planets are thought to be remnants from the early Solar System, and their study can help us understand the conditions that existed during that time.
In conclusion, dwarf planets are a category of celestial objects that share similarities with planets but have not cleared their orbit of other debris. There are currently five recognized dwarf planets in our Solar System, including Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, and Ceres. The study of dwarf planets is important for understanding the history and evolution of our Solar System.