By Shashikant Nishant Sharma
Social control is the process by which a society regulates the behavior of its members. It's a way to maintain order and stability, and to prevent negative behavior that could harm others.1. Understanding Social Control
Social control refers to the mechanisms, strategies, and institutions that societies use to regulate individual and group behavior to maintain order and social cohesion. It ensures that individuals conform to societal norms, values, and laws, thereby preventing deviant behavior and promoting stability. Social control is essential for the smooth functioning of a community, as it creates a balance between personal freedoms and collective interests.
2. Types of Social Control
Social control can be broadly categorized into two types:
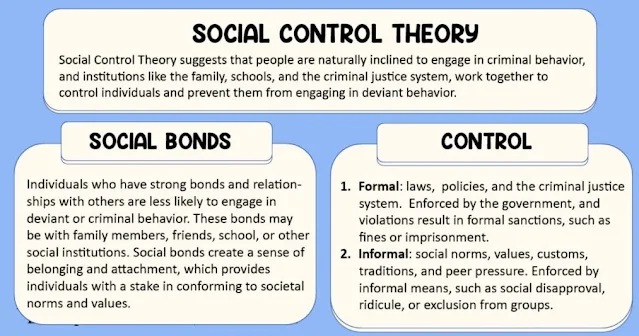
- Formal Social Control: This involves established institutions such as the legal system, law enforcement agencies, and government regulations that enforce rules through laws, policies, and punishments.
- Informal Social Control: This includes unwritten norms, customs, traditions, and societal expectations that guide behavior. It operates through social institutions like family, religion, and peer groups.
3. Mechanisms of Social Control
Several mechanisms help maintain order and cohesion in communities. These include:
A. Legal and Political Mechanisms (Formal Control)
- Laws and Regulations – Governments establish legal frameworks that define acceptable behavior and prescribe penalties for violations.
- Law Enforcement – Police, courts, and correctional institutions ensure compliance with laws and administer justice.
- Government Policies – Public policies and governance structures regulate behavior in economic, social, and political spheres.
B. Social and Cultural Mechanisms (Informal Control)
- Norms and Values – Societal expectations shape behavior by defining what is considered right or wrong.
- Family and Socialization – Parents, relatives, and community elders teach norms and values, reinforcing positive behaviors.
- Religion and Morality – Religious institutions promote ethical behavior and instill a sense of moral responsibility.
- Education – Schools and universities teach discipline, civic responsibility, and critical thinking.
- Peer Pressure – Friends and social groups influence behavior through acceptance or rejection.
C. Psychological and Emotional Mechanisms
- Guilt and Conscience – Internalized moral standards help individuals self-regulate behavior.
- Public Opinion and Social Stigma – Fear of social rejection discourages deviant actions.
4. Importance of Social Control in Communities
- Maintains Order and Stability – Prevents chaos by ensuring individuals follow common rules.
- Promotes Social Cohesion – Strengthens bonds between individuals through shared values.
- Protects Rights and Freedoms – Balances personal liberties with collective welfare.
- Encourages Positive Behavior – Rewards compliance with norms and discourages deviance.
Conclusion
References
Breed, W. (1955). Social control in the newsroom: A functional analysis. Social forces, 326-335.
Dehalwar, K., & Sharma, S. N. (2024). Social Injustice Inflicted by Spatial Changes in Vernacular Settings: An Analysis of Published Literature.
Horwitz, A. V. (1990). The logic of social control. Springer Science & Business Media.
Janowitz, M. (1975). Sociological theory and social control. American Journal of sociology, 81(1), 82-108.
Ross, E. A. (2017). Social control: A survey of the foundations of order. Routledge.